Are You at Risk for Diabetes? Recognizing the Silent Signs Before It’s Too Late

Dr. Akhila Reddy Regatte
MBBS, DNB (Family Medicine),
PG Dip Diabetes (Cardiff Univ, UK),
PG Dip Endocrinology (Univ of South Wales, UK)
1. Feeling Thirsty All the Time and Frequent Bathroom Trips?
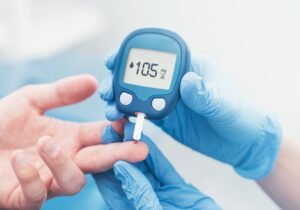
Feeling thirsty means you need a drink, but if you’re constantly thirsty and going to the bathroom a lot, this could be more than just thirst. It might mean that your body is trying to flush out extra sugar through the kidneys. This is an important warning that something could be wrong.
- Constant thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- May indicate excess sugar in the bloodstream
2. Weight Loss Without Trying
Weight loss could seem positive, but without trying, it can be a warning. This happens when your body can’t use sugar properly and starts burning fat for energy. This is not a healthy weight loss method and means an imbalance in your body.
- Unexplained weight loss
- Body burns fat for energy due to inefficient sugar use
- May lead to malnutrition and weakness
3. Persistent Tiredness
Feeling tired all day despite enough sleep might indicate a problem. Your body may not be using sugar effectively, which affects your energy. It’s like driving a car without enough fuel—you might rest enough, but still feel low on energy.
- Low energy despite rest
- Fatigue caused by the body’s inability to use glucose for energy
- May disrupt daily activities and productivity
4. Blurry Vision
Blurry vision may not seem serious, and you might think it’s due to tiredness, but it can signal high blood glucose. If untreated, it could lead to serious eye issues.
- Blurred vision, especially after meals
- Could indicate diabetic retinopathy if left untreated
- High blood glucose levels cause fluid imbalances in the eyes
5. Slow-Healing Wounds
Did you notice healing of cuts is taking longer? This is likely trouble with your body’s healing process. Diabetes is known to slow healing, thus making you more prone to infections. Small unattended wounds can become bigger problems.
- Cuts or wounds that take longer to heal
- Increased risk of infection due to impaired immune response
- Diabetes affects blood circulation and the body’s ability to repair tissues
6. Tingling Sensation / Feeling Numb
Feeling numbness or tingling in your hands or feet might be related to nerve issues. High blood sugar might be the likely culprit. If left unattended, it could lead to permanent damage.
- Tingling or numbness in hands, feet, or legs
- Often caused by diabetic neuropathy
- Can lead to long-term nerve damage if untreated
7. Darkened Skin
Have you noticed dark patches on your neck or any of the skin folds? This is likely a sign of insulin resistance. The dark patches indicate your body isn’t using insulin properly. The patches don’t hurt.
- Dark patches in skin folds (e.g., neck, armpits)
- Commonly seen in people with insulin resistance
- Known as acanthosis nigricans, a sign of poor insulin regulation
8. Frequent Infections
Are you very frequently experiencing UTIs or yeast infections? Frequent infections can indicate the underlying issue. The immune system is weakened by diabetes, making it tough for the immune system to fight infections.
- Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Increased risk of yeast infections
- A weakened immune system caused by high blood sugar levels
9. Dark Circles Around Eyes
Dark circles might suggest you need more sleep. But if they occur regularly, even with enough rest, it could mean fluctuating blood sugar levels. You might feel fine otherwise, but these circles could show insulin resistance.
- Persistent dark circles under the eyes
- May indicate fluctuating blood sugar levels
- Associated with insulin resistance and poor sleep quality
10. High Blood Pressure
Diabetes is known to raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Always monitor blood pressure.
- Increased blood pressure, often due to insulin resistance
- Higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease
- Regular blood pressure checks are essential for diabetic individuals
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, an endocrine disorder, is caused by either insulin deficiency or resistance to the action of insulin at the receptor site—or both. This leads to fluctuating blood sugar levels and eventually affects end organs like the kidney (DKD), liver (CKD), heart (MI), nervous system (diabetic neuropathy), and eyes (diabetic retinopathy), thus affecting the whole body.
- Insulin deficiency or resistance leads to fluctuating blood glucose
- Can impact vital organs like kidneys, liver, heart, eyes, and nerves
- Early intervention can help prevent long-term damage
Factors Contributing to Diabetes
Changed lifestyles, rural-to-urban migration, and a high competitive world all cumulatively lead to ‘stress’ and become major unmodified risk factors, causing diabetes mellitus to become a major noncommunicable disease affecting the quality of life.
- Lifestyle changes, including diet and physical activity
- High levels of stress and fast-paced urban life
- Rising diabetes incidence linked to modernization and dietary changes
Early Identification and Intervention
Early identification and early intervention can prevent total diabetes and even reverse it before the disease becomes permanent.
- Early detection can lead to a reversal or control of diabetes
- Proper management can reduce the risk of complications
- Continuous monitoring of blood glucose is key for preventing long-term damage
When to See a Specialist
If you have two or more of the above symptoms, contact a diabetic specialist for evaluation.
- If you experience multiple symptoms, seek professional help
- Early diagnosis is key to managing diabetes effectively
- A specialist can guide you in managing symptoms and preventing complications
Latest Article
Are You at Risk for (PCOS) Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Early Stages of Thyroid